Satellite data in land use
Remote sensing has provided access to an immense wealth of information in land use. This data has significantly enhanced our understanding of land use patterns and their evolution over time. Thanks to space-based satellite sensors, we are now able to conduct daily global mapping of the Earth's surface.
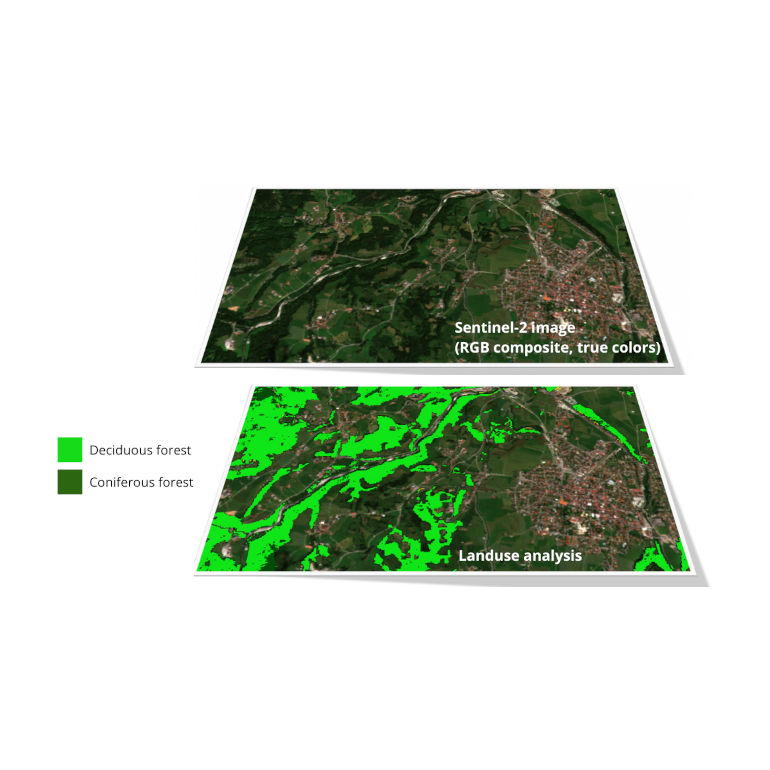
By utilizing images captured by satellites, we can automatically identify various land cover types, including forests, agricultural land, and urban areas. In BitApps, we bring this data accessible and available for everyone, From Space to Pocket.
The use of satellite data
By analyzing satellite imagery and processing in the cloud using AI, we bring up-to-date information continuously available for business purposes via automated services. This becomes particularly significant when ground-based data for an area is limited or inaccessible, such as when conducting research in large areas or hard-to-reach regions. Also, when the situation is continuously changing, such as the situation of forests experiencing the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, satellite imagery can be used to track changes in land use over time, including processes like deforestation and urbanization. By comparing images captured at different points in time, it becomes possible to detect alterations in land use. Our task is to provide this information as an initial step toward comprehending the underlying causes and then facilitate the decision-making process for future actions.
Satellite data can also be used to understand the effects of climate change on land use, forestry, and agriculture. We are able to detect changes in vegetation and gain insights into how ecosystems are being affected by climate change. We deliver the results of this analysis which provide valuable information for professionals in developing more sustainable land-use practices.
But identifying the effects of climate change on land use is not enough. We also provide essential tools to organizations to effectively manage these work processes and to enable the recovery of detected changes before they reach a critical stage.
Satellite data but also other sources
To benefit from the full potential of satellite data, we integrate it with reference measurements collected on the ground (known as ground truth) or through fusion with other remote sensing techniques that provide more detailed information.
When it comes to accurately identifying land use classes, the use of high-resolution aerial imagery proves invaluable, as satellite imagery typically has lower resolution but is more often updated. By incorporating aerial imagery, we can provide a more precise determination of the areas occupied by specific land use classes. This dataset can then serve as a valuable resource for training artificial intelligence or machine learning algorithms.
Using this approach, we have developed algorithms capable of automatically identifying land use classes in new satellite images. The learning process in these algorithms plays a crucial role in classifying the land use categories based on the spectral values recorded in satellite images. The accuracy of such algorithms depends on various factors, including the quality and representativeness of the learning dataset used for training them.
Challenges of using satellite data
While satellite data has numerous advantages for land use analysis, there are still challenges we need to overcome. For example, factors such as cloud cover and atmospheric interference can affect the accuracy of the information provided by satellite imagery.
We take pride in the specialized skills and expertise of our IT teams, who possess the necessary knowledge to interpret satellite data since this expertise may not be easily accessible in all contexts or organizations. Our team's expertise in satellite data analysis empowers us to extract valuable insights from satellite imagery, enabling us to provide our customers with the information they need to make well-informed decisions.
In summary, satellite data remains a valuable tool for monitoring and managing land use, providing precise and timely information. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations associated with satellite data and recognize that its potential for future improvements relies on advancements in technology and addressing the challenges that currently exist.
Satellite data in BitApps
In BitApps we use optical satellite data from the COPERNICUS Sentinel-2 mission, made available by the European Space Agency. This data offers several key advantages, including frequent revisits by the satellite over a specific region, occurring approximately every 5 days, and unrestricted access to the data at no cost.
Currently, we focus on environmental analysis of forest stands for which we provide a Forest Health Map. Thanks to the use of state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms, we can identify forested areas within the satellite images and generate a raster map indicating the health level of each forested region. This approach offers a significant advantage as the forest health information is automatically and continuously updated with the availability of new satellite imagery.
By using the Forest Health Map, we can pinpoint areas where parcels of land are facing challenges such as droughts, insect infestations, and the impacts of climate change. These maps prove invaluable for local forestry organizations as they enable them to closely monitor and manage the parcels under their jurisdiction.


